Introduction to Private 5G Networks

What is Private 5G?
A Private 5G Network is an enterprise-dedicated network tailored to deliver the latest advancements of 4G LTE and 5G technology and drive the digital transformation of businesses and organisations across industries.
Private 5G provides secured communications with high bandwidth, low latency, and reliable coverage to connect people, machines, and devices. Private 5G solutions are ideal for IoT-intensive applications like intelligent manufacturing and sensitive environments like ports and banks.
More securely and efficiently than public 5G and LTE networks, private 5G offers solutions that provide connections to authorised users only within the enterprise and processes the generated data locally, in isolation from the public network. Easy to deploy, operate, and scale to meet all operational needs.
Why Choose Private 5G Over Wi-Fi or Public Networks?
Private 5G networks offer three critical advantages:
- Enhanced Security: Data stays within your enterprise perimeter with zero exposure to public internet traffic.
- Guaranteed Performance: Dedicated bandwidth and ultra-low latency for mission-critical applications.
- Massive Scale: Connect thousands of IoT devices across large areas with consistent coverage.
Key Benefits vs Traditional Networks
Spectrum, Coverage and Speed
The range of a private 5G network can vary from a few thousand square feet to thousands of square kilometres, depending on the power of the radio transmitter, the band used, and the user’s requirements.
A typical 5G radio that operates on low, middle, and high bands provides the following frequency ranges:
- Low Band (600MHz-1GHz): Best coverage, penetrates buildings, 50-250 Mbps
- Mid Band (1-6GHz): Balanced coverage/speed, most versatile, 100-900 Mbps
- High Band (24-100GHz): Highest speeds but limited range, 1-10 Gbps
Deployment Scenarios
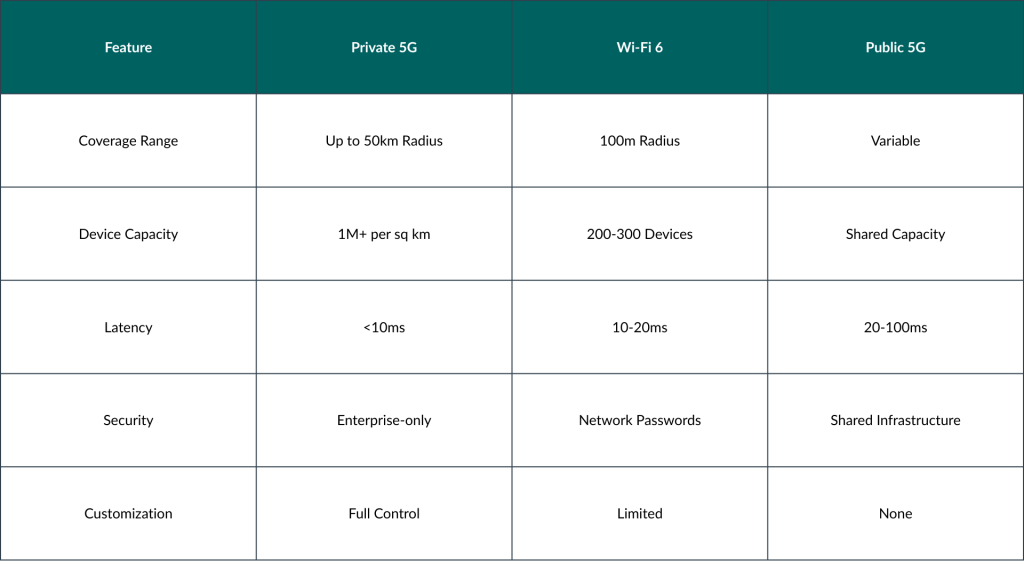
The 5G system is disaggregated into independent components known as “network functions” (NF) that communicate through a standard API. These NFs are accountable for the operation of mobile networks, including authentication, IP address allocation, policy control, and user data management.
Service-Based Architecture makes the 5G system very flexible and able to add new services and applications to meet the needs of any industry.
5G Architecture
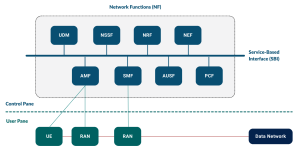
Figure 1: 5G Architecture
Control and User Plane Separation adopted in the 5G architecture allow operators to separate the 5G control function from the data forwarding function.
For example, the control plane can be deployed centrally, whereas the user plane function (UPF) could be deployed flexibly at any location within the network to accommodate the various data processing requirements.
The private 5G network architecture can be deployed in different scenarios to meet each customer’s needs. We can categorise the deployment based on the level of isolation and integration with the public network into three scenarios as follows:
1. Isolated Private 5G Network
Enterprise hosts and operates the 5G network (complete set: gNB, UPF, 5GC CP, UDM, MEC), where the network is physically isolated from the public network. Despite the high cost associated with deploying this scenario, it guarantees complete data security, reduces the likelihood of a data breach, and provides ultra-low latency connections.
Figure 2: Isolated Private 5G
Best for: Banks, government facilities, critical infrastructure.
Pros:
- Complete data isolation from public networks.
- Ultra-low latency (<5ms).
- Full customization control.
- Highest security posture.
Cons:
- Highest initial investment ($500K-$2M+).
- Requires specialized IT staff.
- Full maintenance responsibility.
2. Shared Private 5G Network
A shared private 5G network scenario uses an operator’s public network to reduce installation costs. Based on the business needs, the customer can choose the proportion of components they host and manage locally, and the elements will share with the mobile carrier.
MEC and UPF may be deployed on-site on premises like smart factories, stadiums, and cinemas, enabling a private 5G architecture with minimal latency and future changes. In addition, the business owner can control the radio access network locally to allow quick and reliable connection (RAN).
Best for: Smart factories, stadiums, large campuses.
Pros:
- 60-70% lower deployment costs.
- Carrier handles core maintenance.
- Local control of critical functions.
- Faster deployment (weeks vs months).
Cons:
- Some dependency on carrier infrastructure.
- Limited customization of core functions.
3. Private 5G Over Slicing
Depending on the application’s requirements, a Radio Access Network (RAN) may be installed on-site and connected to the public network via a dedicated data slice that provides private 5G service.
Best for: Temporary deployments, proof-of-concepts, smaller facilities
Pros:
- Lowest upfront costs.
- Fastest deployment (days to weeks).
- Carrier manages all infrastructure.
- Easy to scale up/down.
Cons:
- Least control over network functions.
- Still shares physical infrastructure.
- Dependent on carrier capabilities.
Private 5G Use Cases
Smart Ports and Manufacturing Facilities:
Connect autonomous cranes, robots, drones, legacy machines, or edge gateways within facilities to achieve industrial network service level metrics.
- Manufacturing & Industry 4.0 Applications:
- Autonomous robots coordinating assembly lines in real-time.
- Predictive maintenance using IoT sensors on every machine.
- Quality control with AI-powered vision systems.
- Digital twins for virtual production optimization.
- Ports & Logistics Applications:
- Remote crane operation with HD video feeds and haptic feedback.
- Autonomous vehicle coordination for container movement.
- Real-time cargo tracking throughout facility.
Enable Security Applications:
Connect video cameras, fingerprint scanners, face detection, and automatic licence plate readers to private networks with guaranteed and dedicated bandwidth.
- Enhanced Security Features:
- AI-powered video analytics for threat detection.
- Biometric access control (fingerprint, facial recognition).
- Automatic license plate recognition for perimeter security.
- Drone surveillance with real-time video streaming.
- Enable Smart Operations: Intelligent and secured operations are enabled using various private-tailed applications such as geofencing, digital twins, mobility prediction, and task scheduling.
Implementation Considerations
Network Planning:
- Coverage Mapping: Identify dead zones and capacity requirements.
- Device Inventory: Catalog existing equipment and 5G readiness.
- Application Analysis: Determine bandwidth, latency, and reliability needs.
- Integration Planning: Connect with existing IT/OT systems.
Cost Considerations:
- Initial Investment: $100K – $5M+ depending on coverage area and requirements
- Ongoing Costs:
- Spectrum licensing (if required): $10K-$500K annually..
- Maintenance and support: 15-20% of initial investment annually.
- Staff training and certification: $50K-$200K.
- ROI Timeline: Most enterprises see positive ROI within 18-36 months through operational efficiency gains and reduced downtime.
Getting Started with Private 5G
Step 1: Assess Your Needs
- Audit current network performance and pain points.
- Identify use cases that benefit from 5G capabilities.
- Calculate potential ROI from improved operations.
Step 2: Choose Your Deployment Model
- Budget constraints and technical requirements.
- Security requirements and compliance needs.
- Timeline expectations for deployment.
Step 3: Select Technology Partners
- System integrators with 5G expertise.
- Equipment vendors for radios and core network.
- Software providers for network management and applications.
Step 4: Plan and Deploy
- Proof of concept with limited scope.
- Pilot deployment in controlled environment.
- Full-scale rollout with lessons learned.
Zinkworks and Private 5G
Zinkworks provides a Networked OT Orchestration platform purpose-built for Industry 4.0 and private 5G.
Customers can use various automation solutions and ML-based prediction models developed by Zinkworks to monitor the network’s performance and manage network resources more efficiently and securely.
In addition, customers can create policy and service profiles with customised bandwidth, latency, and quality of service (QoS) to meet every application’s needs.
Frequently Asked Questions:
01 How much does private 5G cost compared to Wi-Fi?
Initial costs are 3-5x higher than enterprise Wi-Fi, but total cost of ownership over 5 years is often comparable due to operational efficiencies.